Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) rich foods
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid that is a primary structural component of the human brain, cerebral cortex, skin, and retina.
It can be synthesized from alpha-linolenic acid or obtained directly from maternal milk (breast milk), fish oil, or algae oil.
Most of the DHA in fish and multi-cellular organisms with access to cold-water oceanic foods originates from photosynthetic and heterotrophic microalgae and becomes increasingly concentrated in organisms the further they are up the food chain. DHA manufactured using microalgae is vegetarian.
In organisms that do not eat algae containing DHA nor animal products containing DHA, DHA is instead produced internally from alpha-linolenic acid, a shorter omega-3 fatty acid manufactured by plants (and also occurring in animal products as obtained from plants).
DHA in breast milk is important for the developing infant.
In humans, DHA is either obtained from the diet or may be converted in small amounts from eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). More on docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) here
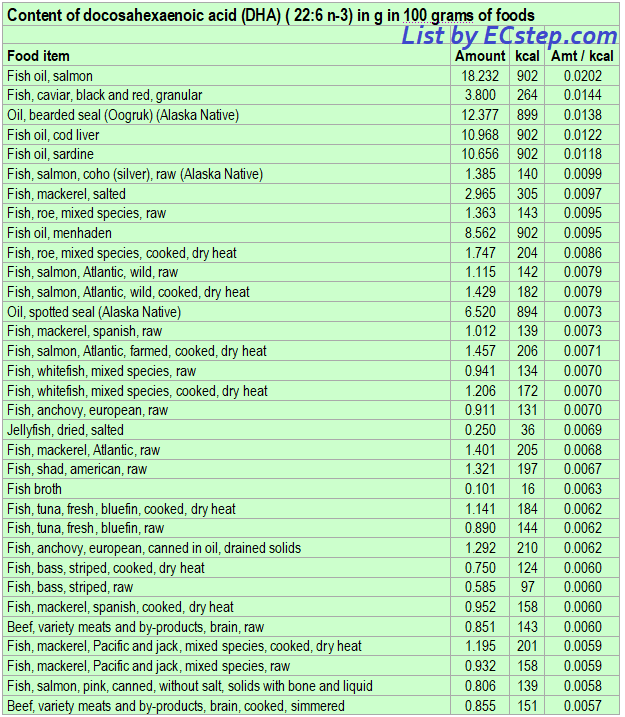
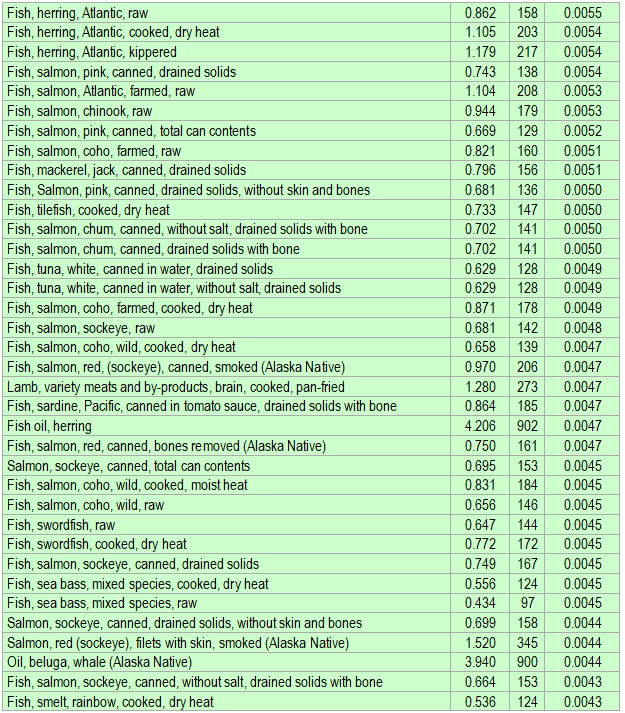
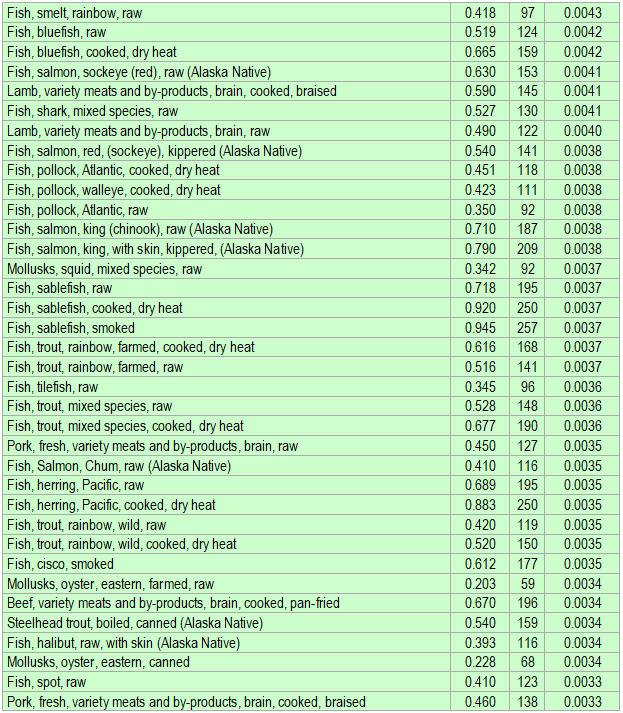
Below is a list of foods having the highest content of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in micrograms (μg) per 100 grams of the food. The list also includes the number of kilocalories (kcal) and the docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) content in micrograms (μg) per kcal, and the list is sorted with respect to the latter with the highest values at the top.
As you can see there are many foods having a high docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) content per kcal. So if you are lacking in docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), you could easily correct the deficiency by eating some of these foods.
The list is made using ECstep’s Personal Nutrition Data Program and includes more than 100 of the docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) richest foods. Commercial brand products are not included in this list.