Vitamin A (retinol) rich foods
4.6/5 (5)
Vitamin A (retinol) is a fat-soluble vitamin that is present in many foods from animal sources, including dairy products, fish, and meat (especially liver).
The vitamin is important for normal vision, the immune system, and reproduction and also helps the heart, lungs, kidneys, and other organs work properly. More on vitamin A here.
Beta-carotene, alpha-carotene, and beta-cryptoxanthin are provitamins, which are transformed in the body into vitamin A. These provitamins are found in fruits, vegetables, and other plant-based products.
The average daily recommended amount of vitamin A in micrograms (mcg or μg) of retinol activity equivalents (RAE) depends on your age and gender being 700 mcg for adult females and 900 mcg for adult males. Children need smaller amounts.
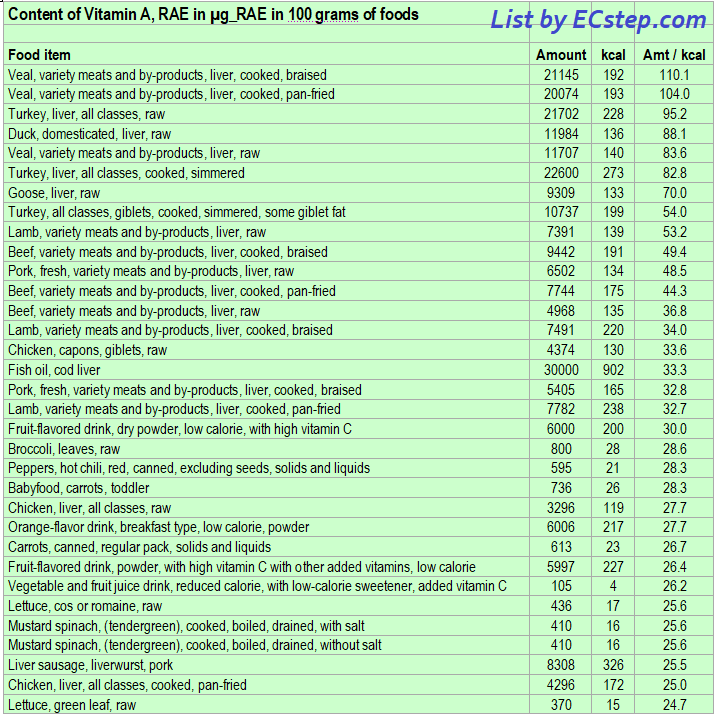
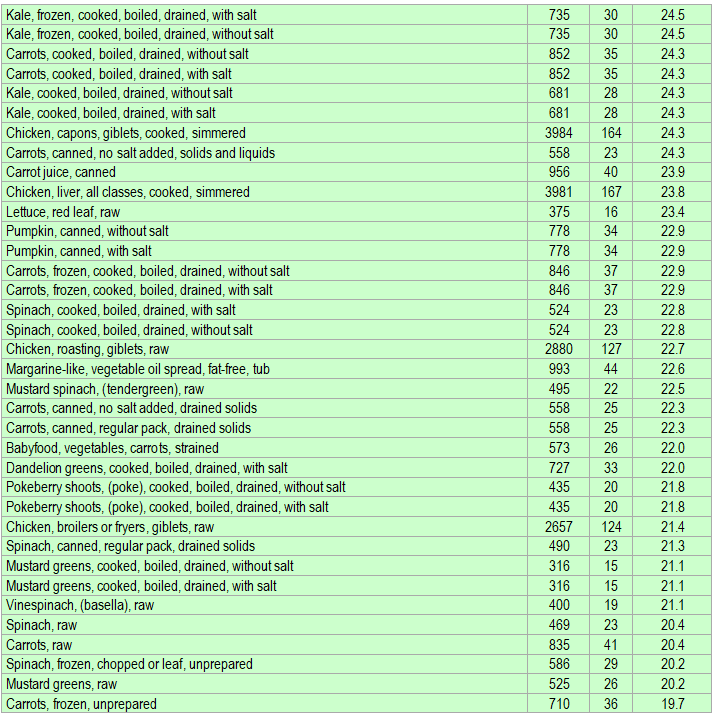
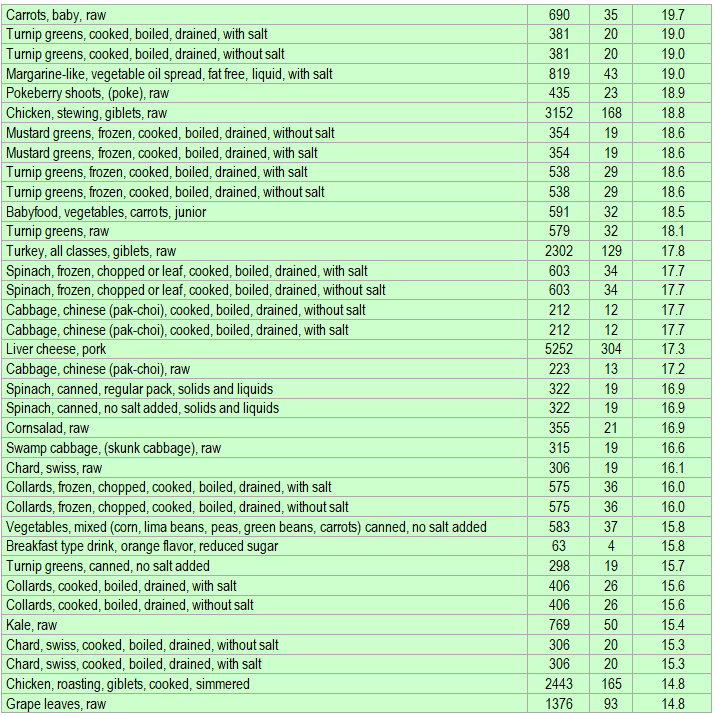
Below is a list of foods having the highest content of vitamin A in micrograms (μg) per 100 grams of the food. The list also includes the number of kilocalories (kcal) and the vitamin A content in micrograms (μg) per kcal, and the list is sorted with respect to the latter with the highest values at the top.
As you can see there are many foods having a high vitamin A content per kcal. So if you are lacking in vitamin A, you could easily correct the deficiency by eating some of these foods. Rather small amounts should be sufficient in most cases.
You should remember that vitamin A can be toxic if very large amounts are ingested repeatedly.
The list is made using ECstep’s Personal Nutrition Data Program and includes more than 100 of the vitamin A richest foods. Commercial brand products are not included in this list.
–
Beta-carotene rich foods
Beta-Carotene is an organic, strongly colored red-orange pigment abundant in fungi, plants, and fruits. It is the most common form of carotene in plants and a precursor to vitamin A.
Excess beta-carotene is predominantly stored in the fat tissues of the body.
The most common side effect of excessive beta-carotene consumption is carotenoderma, a harmless condition that presents as a conspicuous orange skin tint arising from the deposition of the carotenoid in the skin.
Carotenodermia is quickly reversible upon cessation of excessive intake.
The proportion of carotenoids absorbed decreases as dietary intake increases.
Within the intestinal wall, beta-carotene is partially converted into vitamin A.
This mechanism is regulated by the vitamin A status.
If the body has enough vitamin A, the conversion of beta-carotene decreases.
Therefore, beta-carotene is a safe source of vitamin A and high intakes will not lead to vitamin A toxicity.
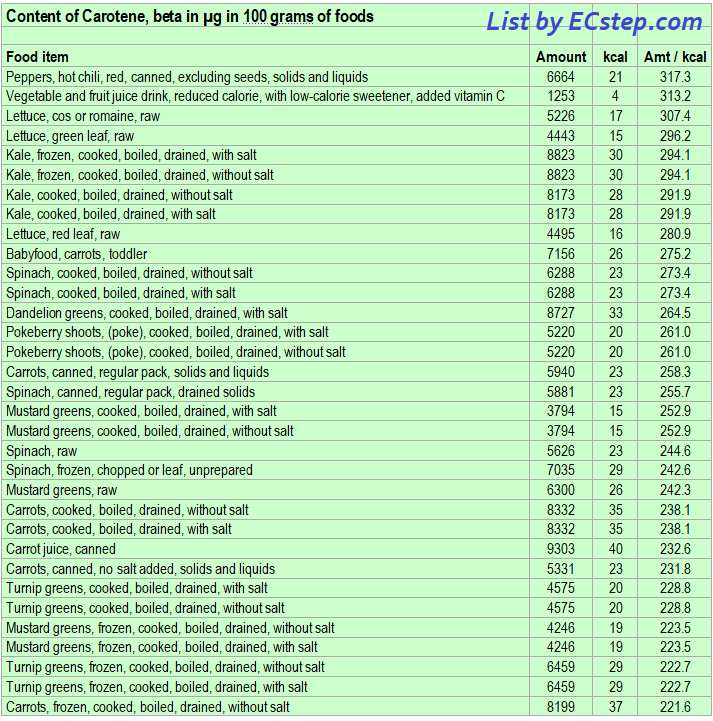
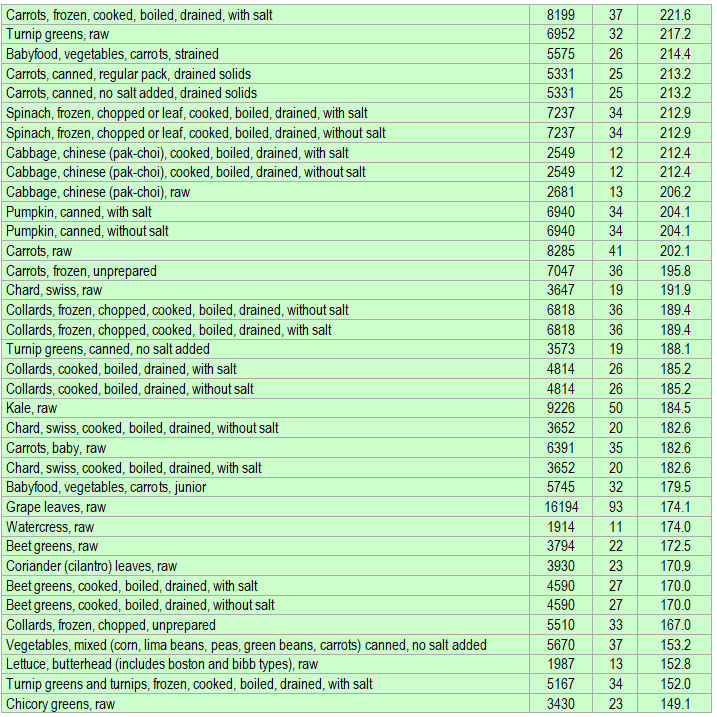
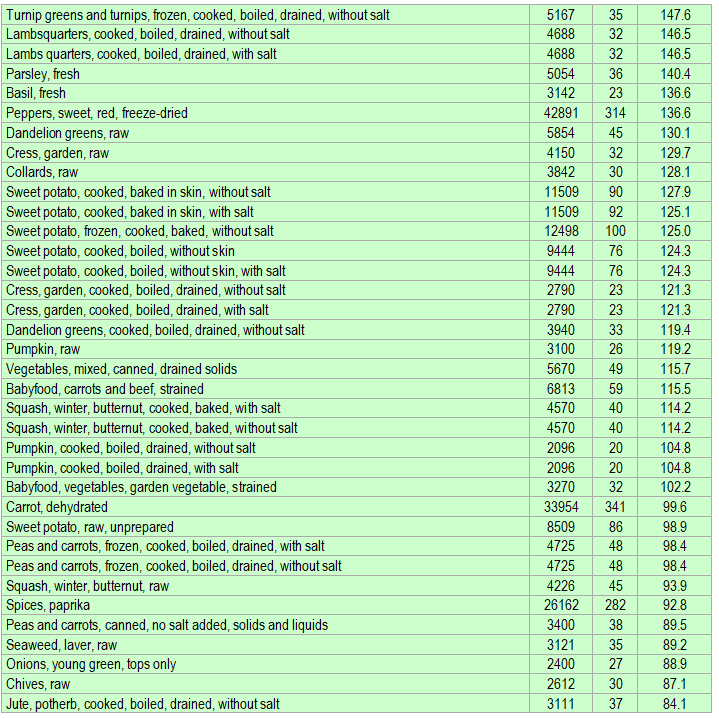
Below is a list of foods having the highest content of beta-carotene in micrograms (μg) per 100 grams of the food. The list also includes the number of kilocalories (kcal) and the beta-carotene content in micrograms (μg) per kcal, and the list is sorted with respect to the latter with the highest values at the top.
The list is made using ECstep’s Personal Nutrition Data Program and includes more than 100 of the beta-carotene richest foods. Commercial brand products are not included in this list.
–
Alpha-carotene rich foods
Alpha-carotene is another carotenoid that also has provitamin A activity.
Like other carotenoids, it has antioxidant and possibly anti-carcinogenic properties, and may enhance immune function as well.
Some studies have found that higher alpha-carotene intake is associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Alpha-carotene is usually associated with ample amounts of beta-carotene when found in fruits and vegetables.
Alpha-carotene’s concentration is especially high in orange carrots and high serum concentrations are associated with carrot intake.
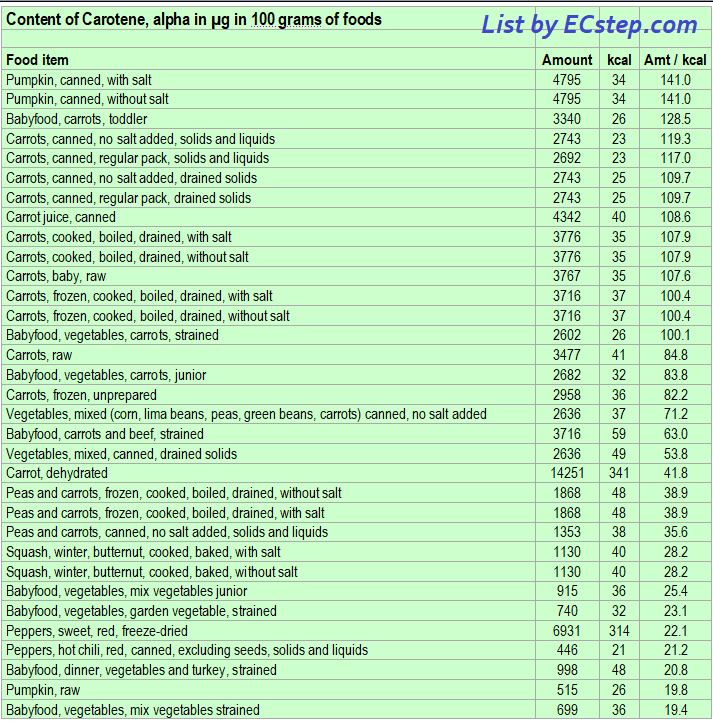
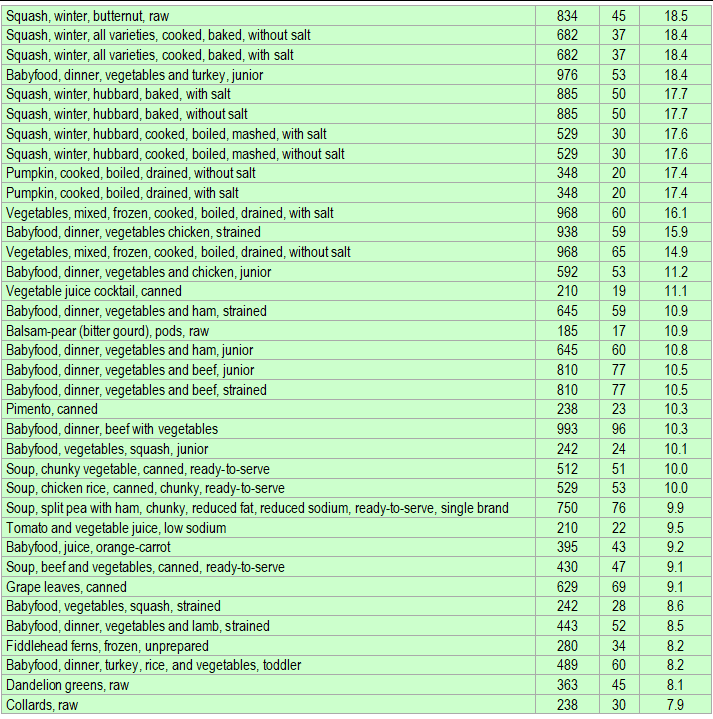
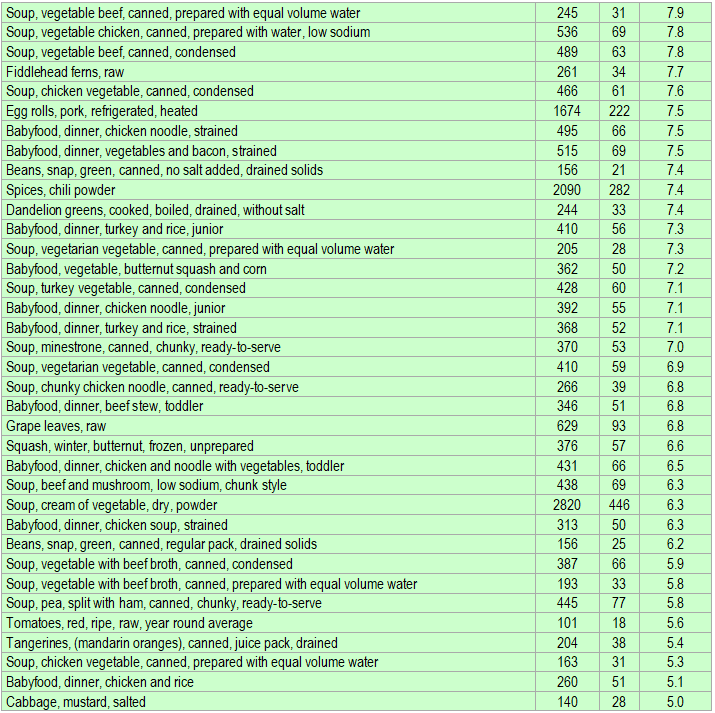
Below is a list of foods having the highest content of alpha-carotene in micrograms (μg) per 100 grams of the food. The list also includes the number of kilocalories (kcal) and the alpha-carotene content in micrograms (μg) per kcal, and the list is sorted with respect to the latter with the highest values at the top.
The list is made using ECstep’s Personal Nutrition Data Program and includes more than 100 of the alpha-carotene richest foods. Commercial brand products are not included in this list.
–
Beta-cryptoxanthin rich foods
Beta-cryptoxanthin is a natural carotenoid pigment, which is closely related to beta-carotene. It is a member of the class of carotenoids known as xanthophylls.
In the human body, beta-cryptoxanthin is converted to vitamin A and is, therefore, considered a provitamin A.
As with other carotenoids, beta-cryptoxanthin is an antioxidant and may help prevent free radical damage to cells and DNA.
Recent findings of an inverse association between beta-cryptoxanthin and lung cancer risk in several observational epidemiological studies suggest that beta-cryptoxanthin could potentially act as a chemopreventive agent against lung cancer.
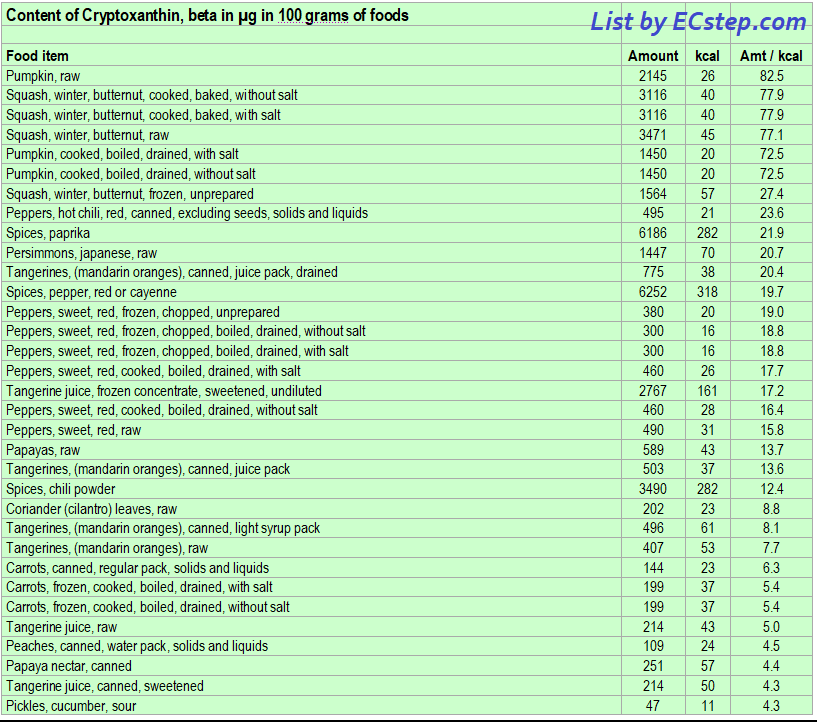
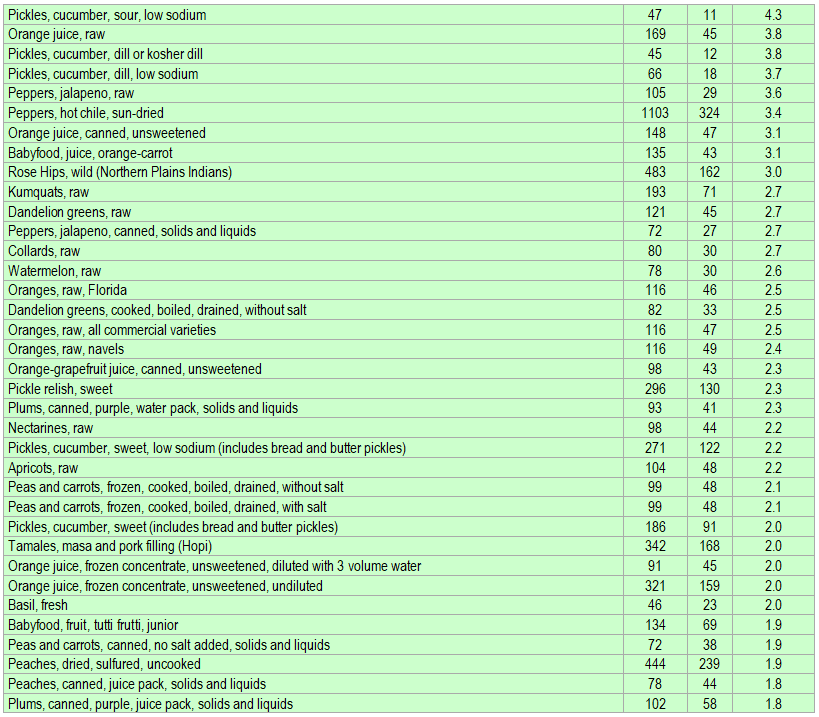
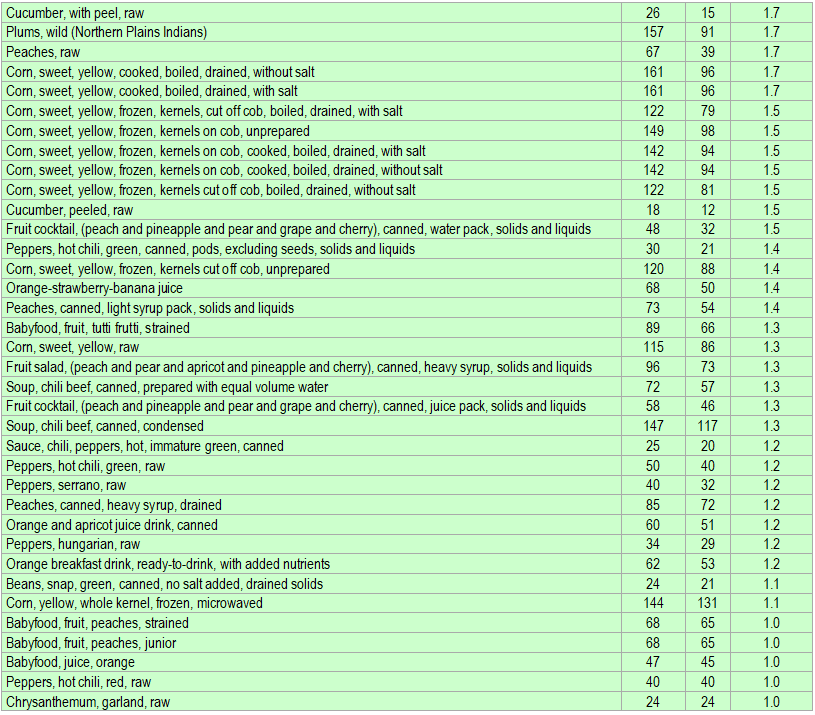
Below is a list of foods having the highest content of beta-cryptoxanthin in micrograms (μg) per 100 grams of the food. The list also includes the number of kilocalories (kcal) and the beta-cryptoxanthin content in micrograms (μg) per kcal, and the list is sorted with respect to the latter with the highest values at the top.
The list is made using ECstep’s Personal Nutrition Data Program and includes more than 100 of the beta-cryptoxanthin richest foods. Commercial brand products are not included in this list.